What is a high Tg PCB?

Glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature at which a substrate transitions from a glassy, rigid state to a rubbery state. High Tg boards are specifically designed to operate at high temperatures. A PCB is considered a high Tg board if its Tg is higher than 180 °C.
Standard FR-4 boards have a Tg of around 130 to 150 °C. High-temperature PCBs offer better mechanical and chemical resistance to heat and moisture compared to FR-4. Higher the Tg value, the better the temperature resistance of the material.
Significance of glass transition temperature
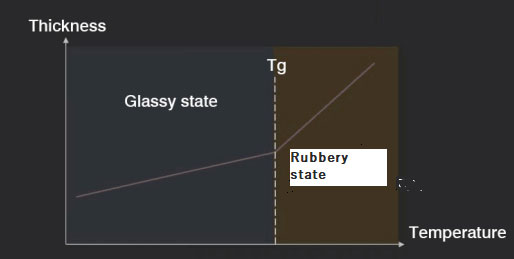
When the board temperature rises above the Tg value, the substrate undergoes structural changes. Due to this, the circuit board will lose its mechanical and electrical properties. This results in various board failures. The circuit board returns back to its initial stage once the temperature reduces below Tg.

PCB Material Design Guide
9 Chapters - 30 Pages - 40 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Basic properties of the dielectric material to be considered
- Signal loss in PCB substrates
- Copper foil selection
- Key considerations for choosing PCB materials
Download Now
Why choose high Tg PCB materials?
When it comes to board design, the operating temperature plays an important role as it directly impacts the reliability. High Tg materials can be used in both rigid and flex boards. Following are a few reasons to choose high Tg PCBs over standard boards.
- High Tg boards are generally more reliable than the standard FR-4 boards as they offer better thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties. This reduces the chances of short circuits and various other board failures in a high-temperature environment.
- HDI/multi-layer boards include complex electronic circuits and dense components. Here heat generation is higher than standard circuit boards. To tackle this drawback, use high Tg materials.
When is it necessary to use a board with a high Tg?
If the circuit has to operate at 150°C then a material with a Tg greater than or equal to 180°C is preferred. Such requirements are typically seen in mil-spec and space applications.
Characteristics of high Tg PCBs
Tg defines the stability of the circuit board dimensions. Below are a few characteristics of high-temperature boards:
- Increased resistance to heat
- Improved mechanical properties
- Good PTH reliability
- Long delamination durability
- High thermal stress resistance
Applications of high Tg boards
These boards are generally used in the following industries:
Metal industry: A metal must be cut, ground, welded, and melted to achieve the desired shape. The temperature in this procedure is extremely variable. High-Tg PCBs are essential to keep the microcontrollers of these devices in perfect working order.
Aerospace and automobile industries: Whether in the aerospace or automotive industries, reliable motor controllers are required to improve engine efficiency. The temperature of the unit rises significantly as the RPM and running hours increase. In these kinds of applications, High-Tg boards are required to withstand higher temperatures.
High Tg materials used at Sierra Circuits
| Manufacturer | Material | Tg value |
|---|---|---|
| Isola | FR370HR | 180°C |
| Isola | P95 | 260°C |
| Isola | I-Speed | 180°C |
| Isola | I-Tera MT40 | 200°C |
| Isola | Tachyon-100G | 192°C |
| Nelco | N4000-13SI | 210°C |
| Nelco | N4800-20 | 180°C |
| Rogers | N4380-13RF | 200°C |
| Rogers | RO4350 B | 280°C |
| Rogers | RO4003 C | 280°C |
The difference between standard FR-4 and high Tg materials is that the high Tg PCB substrate will perform better in terms of mechanical strength, dimensional stability, adhesiveness, water absorption, and thermal management.