Contents

On-demand webinar
How Good is My Shield? An Introduction to Transfer Impedance and Shielding Effectiveness
by Karen Burnham
A critical part of PCB manufacturing is to protect the board from adverse environmental conditions by using various treatments and coatings. A conformal coating is one such process that involves applying a thin, polymeric, and non-conductive film “conforming” to the surface of the board. It is applied to protect the PCB from moisture, dust, and temperature variations.
There are several ways of applying the coating, such as brushing, spraying, dipping, and vapor deposition. The physical, chemical, and electrical properties define the selection criteria of the materials.
What is conformal coating?
A conformal coating is a protective film applied to a circuit board that creates a barrier between the contaminants and the board. It acts as an insulation layer and protects the PCB surface simultaneously.
Some coatings have a hard texture, while others have a rubbery texture. The conformal coatings are in a liquid state before the application. These coatings consist of different materials such as acrylics, polyurethanes, silicons, epoxy, or combinations of resins.

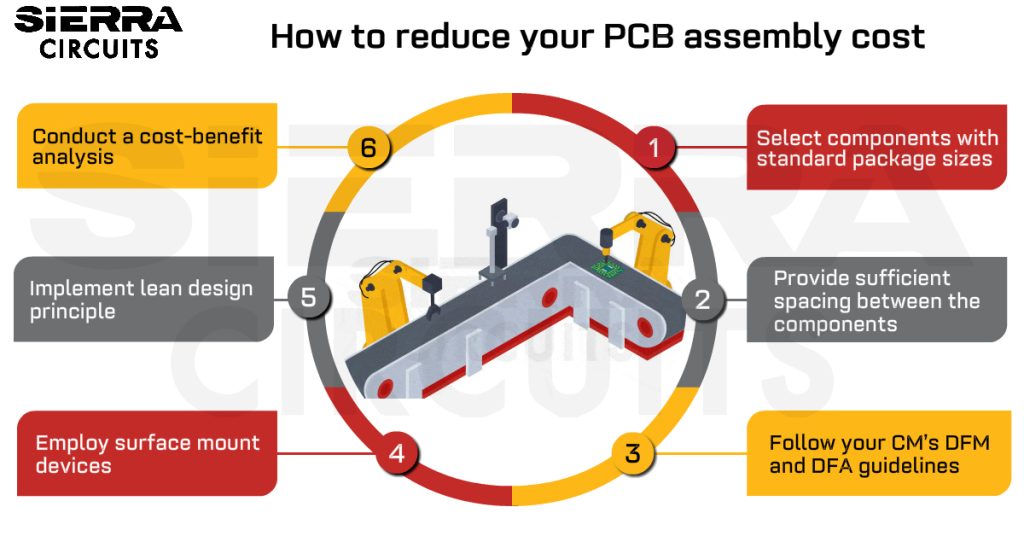
To learn how to design a cost-efficient PCB without board respins, download our DFM eBook.

Design for Manufacturing Handbook
10 Chapters - 40 Pages - 45 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Annular rings: avoid drill breakouts
- Vias: optimize your design
- Trace width and space: follow the best practices
- Solder mask and silkscreen: get the must-knows
Download Now
Why is a conformal coating used?
Conformal coating can perform the following functions:
- The coating offers high insulation protection, resulting in closer conductor spacing.
- It acts as a resistant barrier to moisture and humidity, reducing a leakage current, crosstalk, and electrochemical migration across the board.
- It protects the board from corrosion from chemical and corrosive attacks. Moreover, it prevents damage from rough handling and thermal and mechanical stress.
- The coating can increase the strength between dielectric conductors.
- The coating provides a barrier against particulate contaminants reaching the board surface.
Also, read The importance of PCB line spacing for creepage and clearance.
How to apply conformal coating?
There are many ways to apply the coating.
Brushing
The application of a conformal coating using a brush is a common practice. This is a simple process but requires a skilled operator to ensure the proper quality and finish of the coating. It requires a brush, a container for storing the coating, and a defined area for the application. The brush is dipped in the coating material and applied to the board.
The factors affecting the brushing method quality are the type of brush, operator skill, coating viscosity, environment, and coating material. It offers advantages like low setup, simplicity, and fewer process control requirements. This method is suitable for low-volume production and rework.
Spray application
This technique involves spraying with aerosols, batch spraying, and selective spraying.
- Aerosols: An aerosol consists of a spray gun. It is a solvent-based coating. Spraying aerosols within a spray booth is a cost-effective method. The low setup cost, high process speed, simplicity, and quality of finish make this process better than brushing.
- Batch spraying: Batch spraying uses a compressed air spray gun and gives an excellent quality finish to the coating. The setup requires a spray gun, a spray booth, and an air compressor. Setting the spray gun with the correct atomization pressure and material feed is critical. Blending the coating to the right viscosity is also important. It offers advantages such as low setup cost, flexible process suitable for multiple coatings, etc.
- Selective spraying: Selective spraying only coats the specific areas. The coating is not applied to the areas that require masking, such as connectors and other components. A specialized robot system uses different spray patterns for coating. The valve selection, material, and configuration of the board are critical factors. It is necessary to choose the correct spray valve and coating viscosity.
The spray technique supports all conformal coatings, and programming for this method requires significant technical skills. Therefore, the capital investment is high for spray application. Also, the material performance over time and control environment changes require monitoring.
Dipping
This is a traditional method in which the PCBs are dipped into a coating liquid tank. The variables controlling the process are the speed of immersion, dwell time of the coating, and the board’s withdrawal speed. For dipping, solvent-based conformal coating like acrylics and urethanes is preferred. It is a high-speed process that can be done in batch and inline productions.
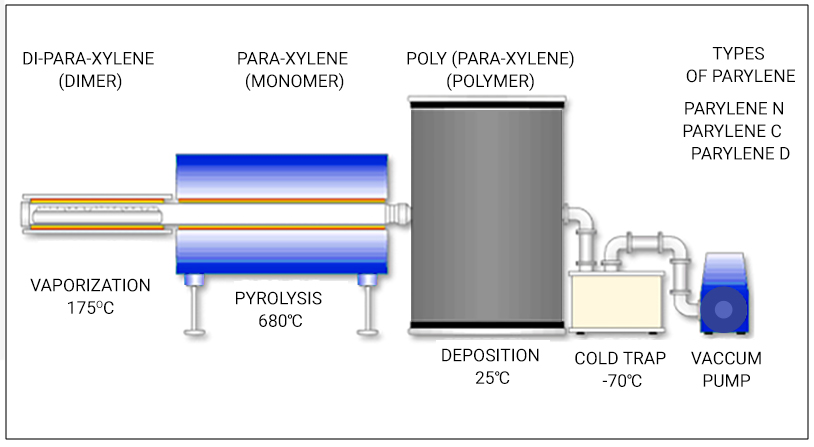
Vapor deposition
A different process deposits the coating in the form of gas on the board. Parylene (p-xylylene polymers) is a process of chemical deposition of the polymers. It is a coating deposited as a gas in a vacuum chamber. It comprises four stages:
- Parylene vaporization
- Pyrolysis
- Coating deposition
- Cold trap
It is an expensive process best suited for medium and high production volumes. Surface preparation is complex in this process. Vapor deposition gives excellent protection against moisture and superior electrical properties compared to other coatings.
The production process for conformal coating
There are eight key steps involved in the production process for conformal coating.
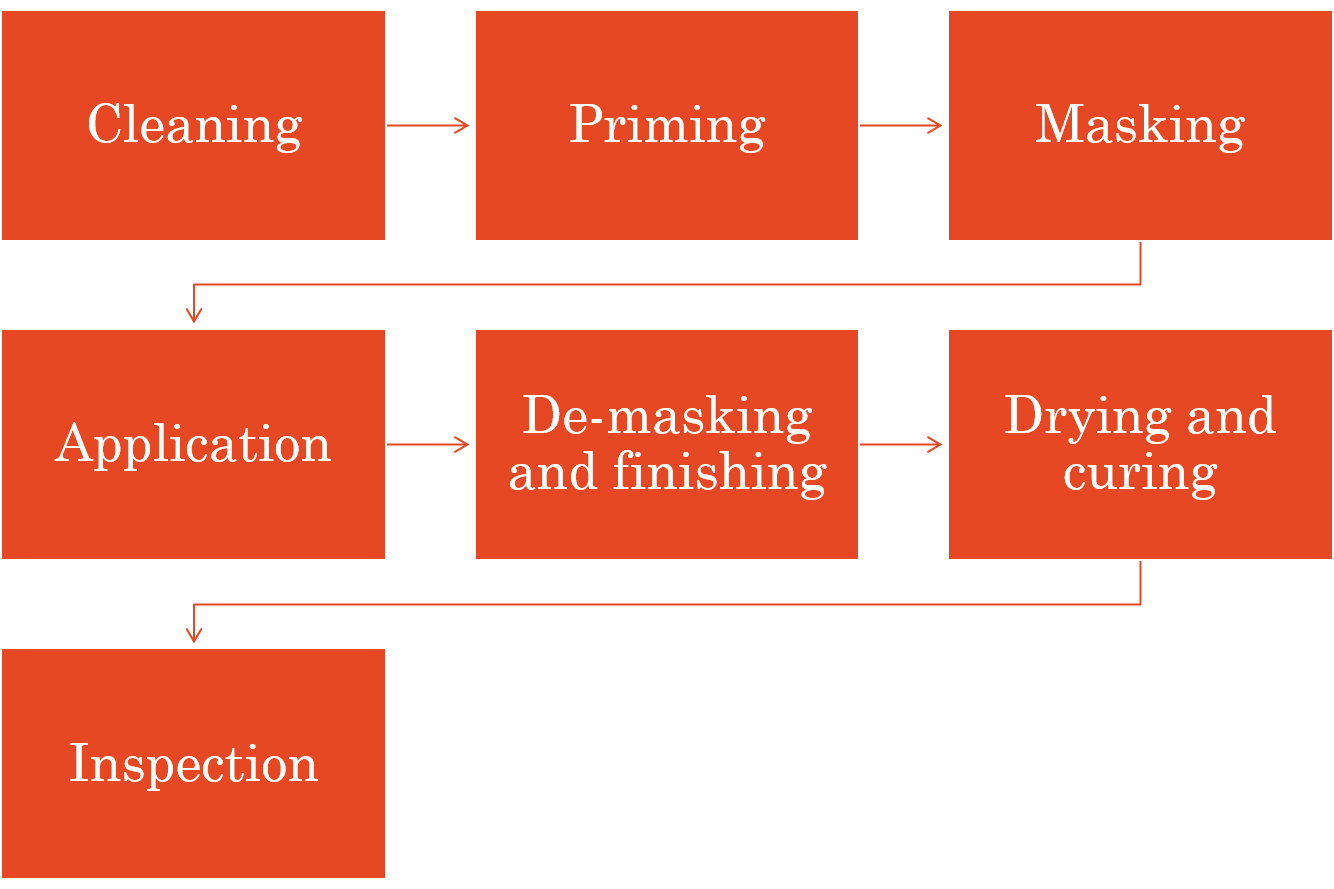
Cleaning
The cleaning removes different residues from the operator handling, soldering, machine, and environmental contamination. The cleaning techniques include:
- Aqueous chemistries
- Solvent cleaning
- Plasma cleaning
There are some tests to validate cleanliness, which include:
- Ionic contamination testing
- Ion chromatography
- Surface insulation resistance
Priming
Primer is a preparatory coating applied on a board before conformal coating, and this process is called priming. It ensures better adhesion and forms a binding layer to retain the coating. The requirement for the priming differs as per the type of resin.
- Acrylic and polyurethane: The wetting and adhesion of these coatings are sufficient to achieve good results, so most of these don’t need priming.
- Silicone conformal coating: Many silicone coatings use primers to enhance the process.
- Parylene coatings: The priming process for the parylene can be a gas phase deposition or a liquid process.
Masking
The purpose of masking is to keep the components and designated board areas from being applied with conformal coating. Specific areas on the circuit board must remain uncoated due to the insulating nature of the coating. Different masking materials include:
- Masking tapes, dots, and shapes
- Liquid latex
- Masking boots
Proper material selection is important to avoid masking failure.
Application
As discussed earlier, conformal coating is applied using various methods such as brushing, spraying, dipping, and vapor deposition.
De-masking and finishing
Masking removal is done after the coating. Next, finishing is implemented to ensure :
- Quality of coating
- Prevention of masking leakage
- Verification of standards
- Prevention of coating defects
The defects are identified, repaired, and sent for the next step.

Drying and curing
It is necessary to understand the difference between drying and curing.
- Drying: This ensures that the PCB is coated and ready to be handled by the operators. It can take a few minutes to several days.
- Curing: This ensures that the coating reaches its desired properties (electrical and mechanical) and protects the board during operation.
The three stages include tack drying, drying to handle, and curing. There are different mechanisms for curing as follows:
- Heat cure
- Moisture cure
- UV cure
- Catalytic cure
Inspection
This is the most important step in the conformal coating process. It includes manual inspection, UV lamp visibility, and automated optical inspection (AOI).

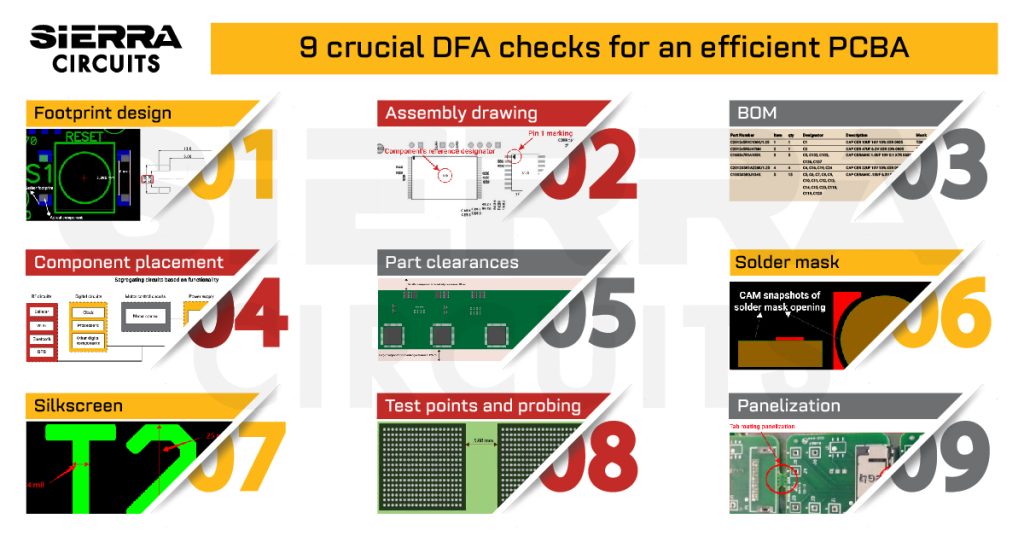
To learn how to select the right materials for your PCBs, download our eBook.

PCB Material Design Guide
9 Chapters - 30 Pages - 40 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Basic properties of the dielectric material to be considered
- Signal loss in PCB substrates
- Copper foil selection
- Key considerations for choosing PCB materials
Download Now
Conformal coating chemistries
Based on the application of the conformal coating, multiple chemistries are available.
Acrylic (organic liquid)
- Easy rework
- Simpler drying process
- Good resistance to moisture
- Easy viscosity adjustment
Polyurethane (organic liquid)
- Good dielectric material properties
- Abrasion resistance
- Solvent resistance
- Good moisture resistance
Epoxy (organic liquid)
- Good dielectric properties
- Higher Tg (glass transition temperature)
- More effective at 150℃
- Good abrasion resistance
Silicon (Inorganic liquid)
- Steady over a wide temperature range
- High Tg
- Solvent resistance
- Good dielectric strength
How to remove the conformal coating from PCB?
There are different methods to remove unwanted conformal coating.
Localized removal of conformal coating
It is the method that removes the conformal coating on a small area of the board. This can be a cause of any coating defect. There are various alternatives to perform this operation.
- Soldering through the conformal coating: The conformal coating melts when the soldering iron tip makes contact with it. It can cause a cosmetic issue, but the proper material selection can overcome this problem.
- Chemical removal: Applying a solvent or stripping fluid will remove the conformal coating. Applying a solvent using a cotton bud and some mechanical pressure helps remove the coating by dissolving the material back into the solution.
A conformal coating with chemical resistance will not respond to general solvents. It will require more aggressive solvents and stripping agents for the job.
- Mechanical abrasion: A compressed air supply strikes the coating with the particles. The particles gradually wear off the coating. Later, the waste particles require cleaning after removal.
It is an extremely effective method for removing the coating on localized areas on the board.
Complete removal of conformal coating
It is a time-consuming process. It employs two methods: chemical stripping and mechanical abrasion.
- Chemical stripping: In this process, the boards are dipped in a series of tanks that contain the proper composition of stripping fluids. This effectively removes the coating from the PCB.
- Mechanical abrasion: The abrasion system takes much time to remove the entire coating from the board. It is highly suitable for high-value circuit boards.
Conformal coating is a very important step in the PCB assembly process. Much research is being conducted on materials, production processes, and application methods, promising innovations in conformal coating.
Let us know in the comment section if you need more about the conformal coating. We will happily address your concerns.