Contents

On-demand webinar
How Good is My Shield? An Introduction to Transfer Impedance and Shielding Effectiveness
by Karen Burnham
During the 19th century, a car or an automobile was treated as the mechanical marvel, operated by a solid engine with an elegant design. However, the beginning of the 21st century has brought substantial changes to the automotive sector. Suddenly, major specs of a vehicle, such as power and speed, took a back seat, while luxury and leisure took the front seat. Like it or not, we have moved on with this phenomenal journey. So, pack your backs, let’s drive straight into a detailed discussion on automotive sensors.
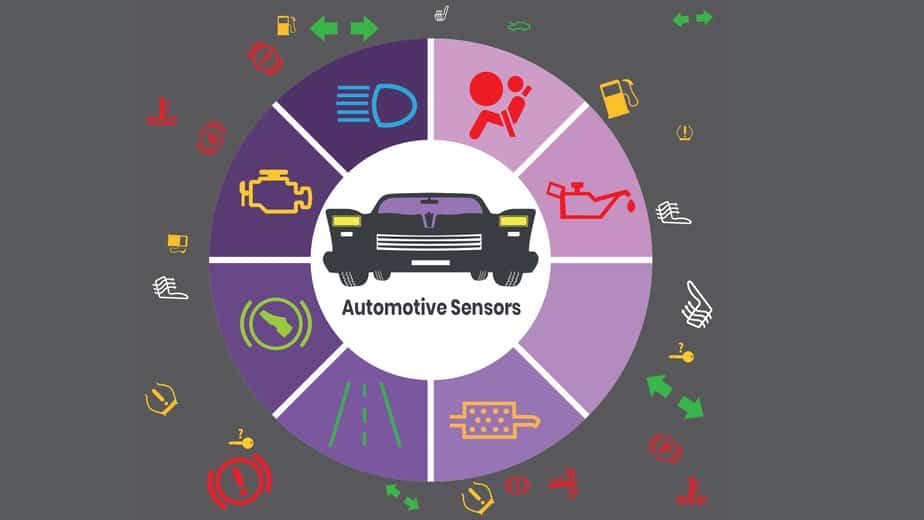
Today’s vehicles are equipped with a wide range of sensors that offer high-level performance, safety, comfort, and convenience. These sensors provide critical data to the user, thus allowing required level safety and comfort. For instance, calculating absolute pressure on the inlet manifold valve for early ignition is considered as the first and most important application of sensors in an automobile. Some common application of automotive sensor includes identifying the position of the crankshaft and calculating air mass flow, exhaust gas, and engine temperature. These types of sensors help improve powertrain performance of the vehicle. However, the rising adoption of electronically controlled electrically actuated systems on the automobile has created new challenges for automotive industry players.
Brief Analysis of Automotive Sensors Market
Miniaturization and surge of IoT technology are key factors driving the demand for automotive sensors over the last decade. Advanced communication capabilities of vehicles are dependent on real-time data, which is gathered from automotive sensors. Additionally, the integration of automotive sensors does not interfere or affect the basic functionalities of the vehicle. This allows manufacturers to focus on improving safety and security in vehicles.
Furthermore, automation and connected vehicle technologies will likely boost demand for automotive sensors including, 3D sensors, LiDAR sensors, and Radar sensors. These technologies alongside MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) are projected to be the most heavily researched automotive technologies. The connected car allows real-time data transfer, thus assisting in monitoring vehicles and drivers. This has generated substantial buzz among buyers and manufacturers across the globe over the past few years.
Market segments such as passenger cars currently hold a major share of the automotive sensors market. Emerging economies such as the U.S., France, and U.K are leading automotive sensors market. The rising sales of passenger cars and growing market size in terms of value and volume are leading to the increased demand for sensors to improve the performance of cars along with significantly enhancing the safety and reducing emission. Improved automobile infrastructure, and rising in purchasing power of the consumer, and increasing popularity of autonomous vehicles are expected to support market growth.
Application of Automotive Sensors
Sensors are used in all types of automobiles including two-wheelers to heavy-duty vehicles. The use of sensors for application involving in wipers, lighting, dashboard, and sunroof has been common practice over the last decade. While, sensors used for parking, seating arrangements, climate, and tilt alarm recently come into practice. Additionally, several sensors are used for tailgate release, tailgate close, trailer management, rear door, anti-theft alarm, immobilizer, and radio as well. Prevalence of vehicle automation and increasing demand for concept cars, like the Stanford solar car, across the globe will increase demand for automotive sensors. Significant attention is given to the research and development (R&D) activities by several automotive players across the globe. As per BMW, which is a Germany based automobile company, future innovation is focused on improvements in existing designs and efficiency of the vehicle.
In line with recent developments, the introduction of automotive sensors such as MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) sensors, wireless sensors, and radar sensors will likely improve the reliability of autonomous vehicles. The advanced technologies such as “pre-emptive technology” and “Conti APIA” are developed to achieve integrated stability and avoid collisions. Such technologies will likely drive more manufacturers towards automotive sensors. Several automotive sensors are used in emission control, battery control and occupant detection in recent years.
Also read: Automotive PCB: The Chassis of the Modern Automotive Industry
Types of Automotive Sensors
Sensors gather data from external as well as internal sources, which is used to transport passengers safely and efficiently. Vehicle sensors are equipped to sense and respond to the changing external as well as internal conditions. Data gathered from these sources is used to provide the control, adaptation, and response of the vehicle. This improves the overall functionality of the vehicle by increasing safety, comfort, and efficiency. Automotive sensors act as an integral part of the nervous systems in passenger cars and off-road vehicles. Automotive sensors can be designed and developed to meet the required specifications, and customized as per consumer demand.
Here is a list of few important sensors used in regular passenger vehicles:
- Brake sensors: These automotive sensors are adopted for vehicle applications such as travel buses for brake master cylinder position (optional redundancy). Other types of the rotary sensor include brake pedal position detection, contactless brake light switch, and wheel speed sensor.
- Pressure sensors: These automotive sensors are used to monitor the vacuum brake pressure and brake line pressure. Some of these vacuum brake booster sensor and brake line pressure used for ABS/ESC modules.
- Humidity and Temperature Sensors: Several automotive sensors are used to monitor temperature changes along with chassis solutions for roof and convertible switches, and seat position. Humidity and temperature sensors are integrated into HVAC systems for the prevention of windscreen fogging and for energy management.
- Clutch sensors: These sensors are adopted for Permanent-magnetic Linear Contactless Displacement (PLCD) for concentric slave cylinder. These sensors also help to monitor the clutch slave cylinder. Other than clutch sensors rotary sensors allow determining clutch pedal position. Some of these sensors include a contactless switch for the clutch master cylinder and a travel sensor for the clutch master cylinder and Dual Clutch Transmission (DCT).
Different Types of Engine Sensors
- Engine and E-motor Sensors: These types of automotive sensors are adopted for vehicle applications involving positioning. Engine parts such as turbocharger actuator, pneumatic (EGR) Cylinder, and CAM are monitored via position sensors. While the speed of crankshaft is measured for e-motor commutation.
- Exhaust sensors: These sensors are placed near the exhaust chamber to maintain urea quality, level, and temperature. Some of these sensors include urea pump pressure and exhaust gas temperature (EGTS) sensor.
- Transmission sensors: These sensors are adopted for in-vehicle applications that involve all gear / neutral detection for manual transmission (MT). This allows the start and stops functioning in the vehicle. Transmission sensors also monitor transmission during drive mode (travel or rotary) for automatic (AT), variable mode (CVT), and dual-clutch (DCT) mode.
Autonomous Vehicles: A Leap towards Future with Sensory Vision

Autonomous driving or self-driving vehicles are generating extensive buzz across the global landscape over the past few years. It is one of the rapidly advancing technologies, which is also subjected to criticism at the same time. However, improved safety due to the integration of high-end automotive sensors for autonomous vehicles will likely boost the autonomous vehicle market in the near future. Moreover, improved infrastructure, such as roads, highways, bridges coupled with enhanced mobility for children, the elderly, and the disabled, particularly in emerging economies such as China, Brazil, and Mexico are expected to drive consumers towards autonomous vehicles.
Also read, Case Study: PCBs for Automotive Sensors.
We don’t doubt, the technology associated with self-driving cars or autonomous vehicles is complex and highly contentious. Many customers are trying to understand how safe self-driving cars are; at the same time, it is important to figure out how they work and kind of automotive sensors are that are used. These sensors can not only recognize objects on the road but also prevent car accidents. Let’s have look at the type of sensors that are used in autonomous vehicles, which is simplifying and defining autonomous driving.
Camera sensors
The autonomous car uses advanced video cameras to detect and interpret objects, which functions similar to the human eye, and allow to navigate accordingly. These video camera sensors cover all angles, thus allowing a 360° view of the entire surrounding. These automotive sensors can provide a user with a broad picture of traffic conditions around the vehicle. The availability of 3D cameras has created significant curiosity among car manufacturers, thus displaying highly detailed and realistic images. Camera sensors also detect objects and classify them based on position and total distance to them. These sensors also help to differentiate other cars, pedestrians, cyclists, traffic signs and signals, and road markings.
Radar sensors
Radar sensors also called Radio Detection and Ranging sensor, are given high priority due to their several advantages during autonomous driving. These automotive sensors generate radio waves that detect distant objects and calculate the overall distance from the vehicle. The distance measurement is performed in real-time. Different types of radar sensors such as short and long-range radars are deployed based on application and perform different functions. The short‑range (24 GHz) radar allows blind-spot monitoring, lane-keeping assistance, and parking aids. The operation involving automatic distance control and brake assistance is performed by long-range radar sensors with frequency up to 77 GHz.
LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) Sensors
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors work based on a similar principle as that of radar systems. However, Lidar sensors use lasers instead of radio waves. LiDAR sensors not only measure the distances to various objects on the road but also develop 3D images with the help of the detected objects. Also, LiDAR is configured to build a full 360-degrees around the vehicle instead of relying on a narrow field of view.
Future Prospects:
The technological giant such as Google and Uber are developing self-driving vehicles with exclusive features such as rotating roofs. The rotating roofs continuously spin and offer 360° visibility. These vehicles provide precise, in-depth data along with the capability to measure distance up to an accuracy of ±2 cm. An autonomous vehicle consists of a LIDAR system. This LiDAR system contains a combination of automotive sensors such as a laser, scanner, optics, and a specialized GPS receiver. This system provides the necessary comfort and safety as well. Several technological giants are focusing on developing 3D maps that allow the vehicle to navigate through during conjected traffic.
Employing CAN bus architecture guarantees you efficient signal transmission even in harsh environments with high temperatures and vibrations. This feature makes it an ideal choice for automotive designs. A wise man once said every technology has its own pitfalls. Yet, we are looking at a technological marvel (no longer mechanical) that will change how you drive your vehicle completely.

High-Speed PCB Design Guide
8 Chapters - 115 Pages - 150 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Explanations of signal integrity issues
- Understanding transmission lines and controlled impedance
- Selection process of high-speed PCB materials
- High-speed layout guidelines