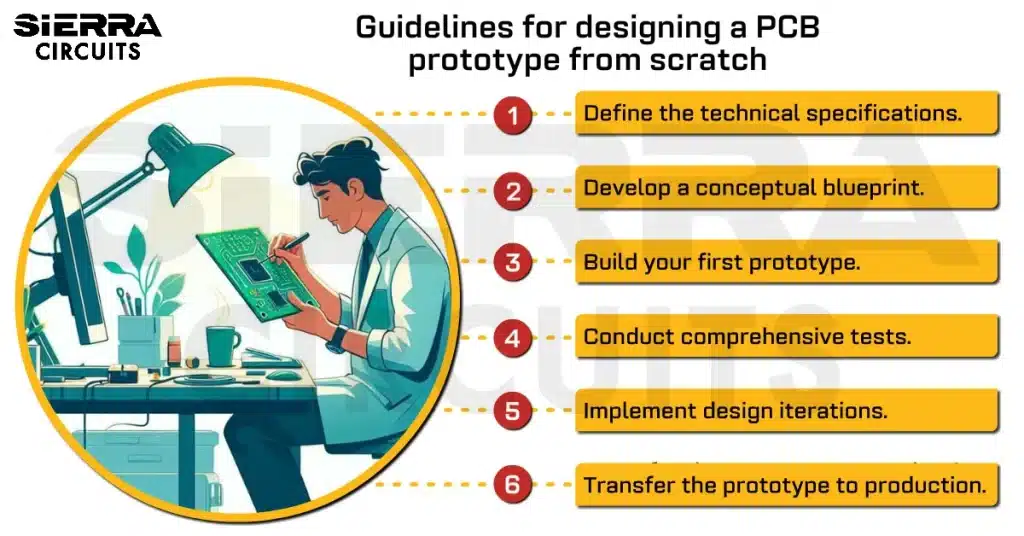
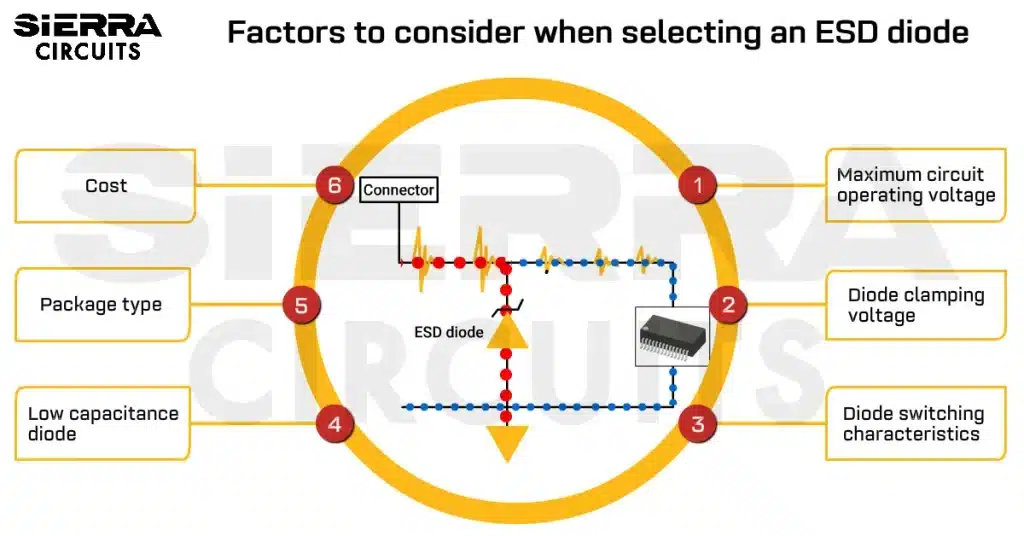
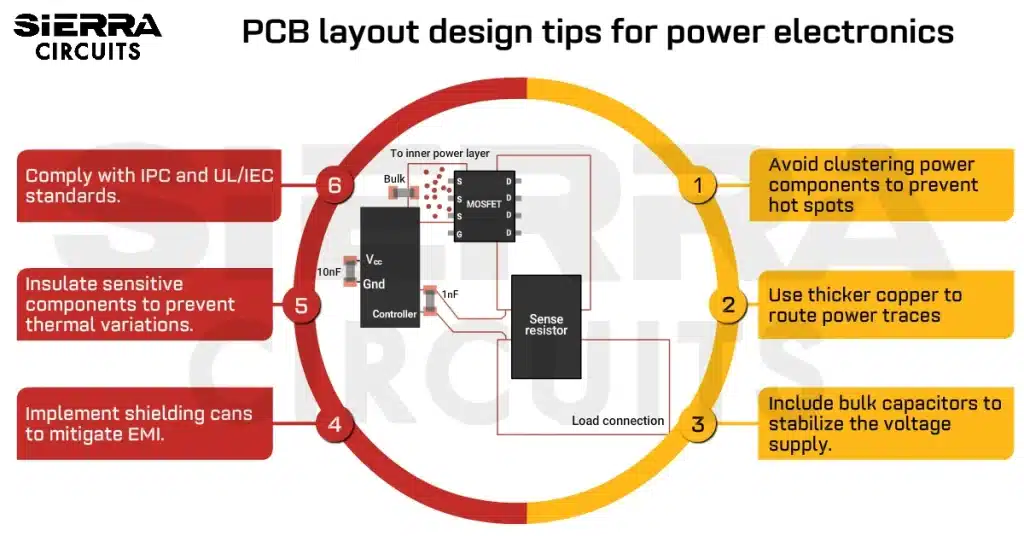
Contents

On-demand webinar
How Good is My Shield? An Introduction to Transfer Impedance and Shielding Effectiveness
by Karen Burnham
The sound vroom… has been turning heads since the time the automobiles hit the streets. The integration of electronics has catapulted the growth of the automotive industry substantially. Buyers look into the luxury features along with the performance of a car or any other vehicle. All these features including the performance of an internal combustion engine are controlled by electronic modules.
The future of the automotive industry looks bright with the ongoing development of self-driven cars, electric vehicles, aerospace and what not. Companies like Tesla are producing automobiles that are not only eco-friendly but also can race a Ferrari. Soon the requirement of gasoline and petrol will disappear and so will the human drivers if everything goes well. The next time you board an Uber, don’t freak out if there’s no one in the driver’s seat- unless it’s the hollow man.
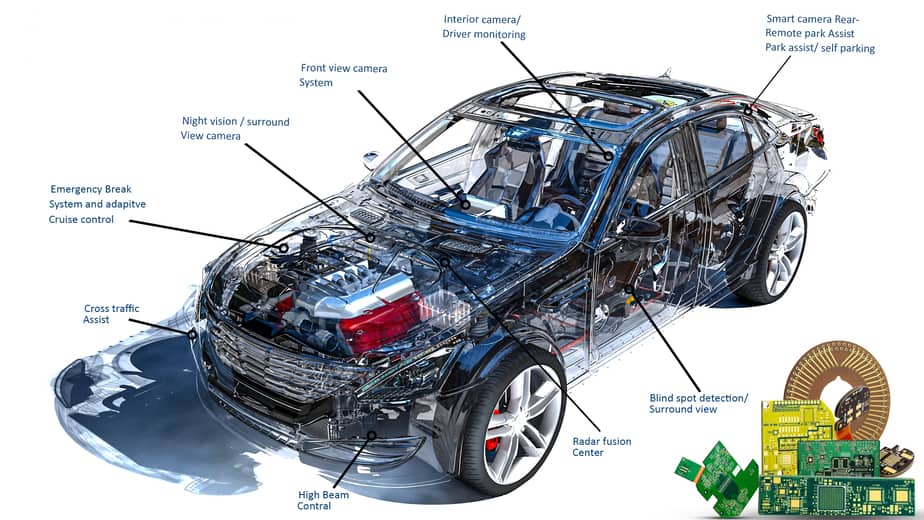
The Impact of PCBs in the Automotive Sector
The growth of the PCB industry in the automotive sector will be rising fast and furious with the focus on the autonomous and electric vehicles. The printed circuit boards are the ones that hold together all the exquisite sensors and the components required for the steady operation of an automotive vehicle.
If you can just stare at a corner and imagine PCB as a chassis of a car, then the engine, the sensors, the axel, the wheels, all form the electronic components that go on the circuit board. Also read, Case Study: PCBs for Automotive Sensors.
When it comes to automotive printed circuit boards, reliability is paramount. They need to survive extreme environmental conditions and vibrations without any setback in performance. On top of this, the boards are expected to be completely operative in the long run as well. The thermal resistance and longevity make an automotive printed circuit board distinct from the rest. The PCB manufacturers are required to be qualified with ISO/TS 16949 which is based on ISO 9001 automotive standards.
So, what are these special types of PCBs made up of? What kind of substrates are utilized? Do they have plenty of heatsinks for heat dissipation? Let’s have a look.
Types of Automotive PCBs
Flex PCBs – These boards are made of flexible plastic substrates. They are composed of PEEK, polyamide, or transparent polyester films. These boards can be twisted and bent. Find their applications around bends and corners in an automobile.
Rigid PCBs – The rigid boards are made of FR4. These boards aren’t flexible. They are usually found in display monitors and reverse cam screens.
Rigid-Flex PCBs – These circuit boards are a combination of Rigid and Flexible boards. They are implemented in lighting systems.
HDI PCBs – These boards feature higher wire density per unit area, finer lines and spaces, and high pad connection density. The HDI boards accommodate more components and play a prominent role in miniaturization. These boards are widely used for infotainment systems.
LED PCBs – The LED boards are made of the aluminum substrate since they require heat dissipation. They can be found in car indicators, headlights, and brake lights.
The Different Substrates that go into Automotive PCBs
- Ceramic Substrate board – The ceramic substrate is made from high-temperature co-fired alumina and aluminum nitride. These boards are implemented in the engine compartment since they can withstand high-temperature variations.
- PTFE PCBs – Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) PCBs tolerate high-frequencies and find their purpose in safety systems and Radar technology.
- Metal Core PCBs – The Metal Core PCBs consist of an aluminum base layer. The base layer is an aluminum alloy sheet on top of which the entire board is built up. The base layer act as a heatsink and thus are suitable for heat transfer applications. The metal core boards provide improved electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. These boards are employed in the Antilock Braking Systems (ABS).
- Heavy copper PCBs – The Automotive printed circuit boards employ thicker copper (Cu) in the outer and inner layers of the boards. These heavy copper boards are preferred over regular ones since they can withstand high temperatures, high frequency, and high current variations. The regular boards display a copper thickness of around 25µm to 50µm. Whereas, the heavy copper PCBs will be 150µm to 200µm thick. These boards are implemented in safety and signaling systems.
With more and more chips being integrated, the material that holds them together will play a prominent role.
Automotive PCBs must qualify for the stringent thermal cycling test, thermal shock test, and temperature humidity test before they are taken into consideration. The boards must restrain from Conductive Anodic Filament (CAF) defects in the dielectric. The CAF can lead to a short between the Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) and the conductive traces.
With the prime focus on autonomous automobiles, the safety of truly driverless cars is debatable. But systems with automatic braking have successfully initiated the brakes when rapidly approaching a stationary vehicle. With microchips that control the engine performance and safety of vehicles, automobiles are getting more dependent on reliable printed circuit boards. All the safety features like drowsy driver alert, and blind-spot detection, require PCBs. It is prudent to incorporate the CAN bus protocol to ease serial communication and reduce the cost and complexity.
Where the PCBs go in Automobiles
- ECL/ECU control modules
- Antilock brake systems
- Digital displays
- Power relays
- Dashboard
- Transmission sensors
- Radar
- Audio systems
- DC/AC power converters
- Engine timing systems
- Electronic mirror controls
- Battery Control System
- Airbag
- LED lighting systems
- Steering
- Engine Control System
- Air Conditioner System
- ABS
The list keeps going on with crucial elements like the navigation unit, entertainment system, and climate control. The growing electric automobile industry requires PCBs specially designed to manage fuel efficiency or battery management systems. Read our blog on 10 automotive PCB design guidelines for a better understanding of design essentials.
From all these things we can incur the fact that the automotive market is lucrative and PCB manufacturers can milk billions out of it. You can also read our case study on design of a motor control board.