Contents

On-demand webinar
How Good is My Shield? An Introduction to Transfer Impedance and Shielding Effectiveness
by Karen Burnham
LiDAR is an emerging technology along the lines of radar and sonar which identifies and maps objects besides terrain. While radar and sonar use radio and sound waves respectively, LiDAR uses pulsed laser light for mapping. This new technology has unlimited potential for applications and holds great promise.
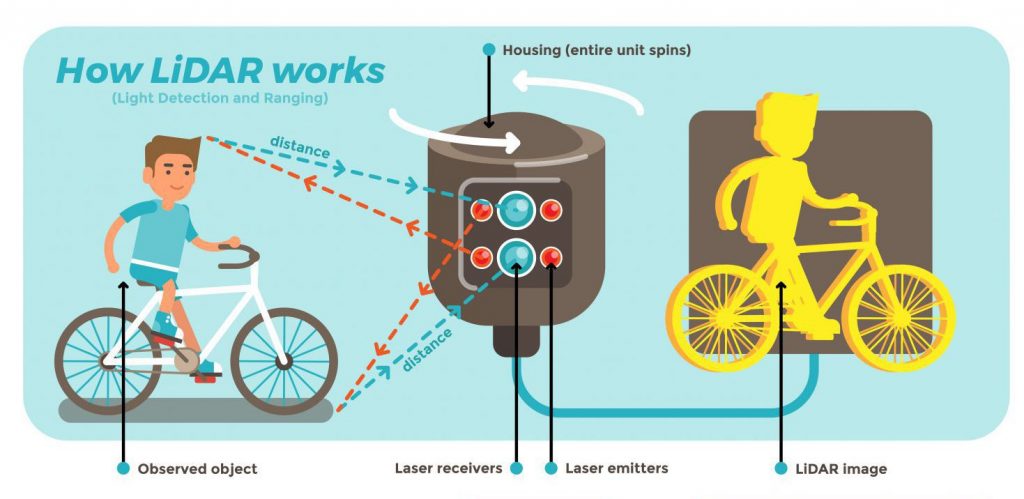
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR stands for light detection and ranging and is a remote sensing system that makes use of pulsed laser light to measure variable distances from objects and terrain. The 3D point data obtained is used to map surfaces and track moving objects.
What are the applications of LiDAR?
LiDAR can be used in any application that requires live object tracking and terrain mapping. This can range from land surveying and transportation to access management for secure facilities.
1. Land surveying
Surveying terrain can be a daunting task without the right instrumentation. LiDAR sensors are compact enough to be mounted or attached to drones for cost-effective mapping of terrain. This is especially useful for areas of rough or complex terrain that might be otherwise challenging to generate 3D terrain models.

2. Power line inspection for maintenance
Periodic maintenance of power lines come with massive safety hazards. These risks can be eliminated by using drone-mounted LiDAR sensors to recognize issues in power lines before they turn into significant problems.
3. Forestry and farming
Large farms can benefit from drone-mounted LiDAR sensors that can be deployed to survey the land and help in deciding better resource allocation. The same approach can be used to monitor the impact of human activity on forest areas with 3D models. This remote sensing method has an edge over other tech in the fact that it can penetrate tree cover while retaining mapping accuracy.
4. Mining
LiDAR is great for generating data on the volume of mineable material in an open mine without disrupting operations on-site. This increases productivity and reduces cost and time overheads.
5. Transport
This is a wide domain ranging from the incorporation of LiDAR units onto vehicles for autonomous driving to city mapping for the planning of mass transit systems.
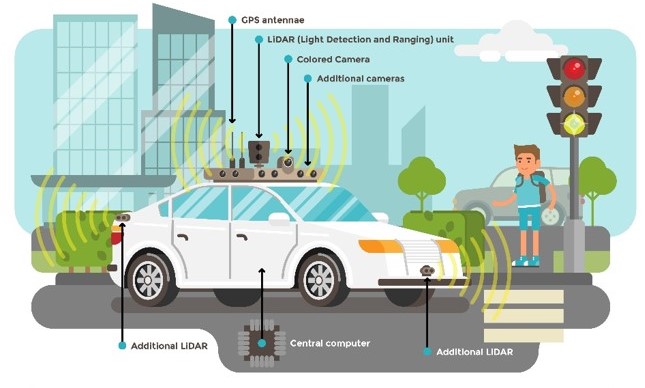
The challenge – vibration resistance and thermal efficiency
The customer we interviewed for this case study is a world leader in 3D sensing and a pioneer in the commercialization of 3D LiDAR. Their AI-driven LiDAR platform is designed for enhancing business process automation for increased productivity. Their mission is to drive business growth for enterprises in turn adding to the quality of life for the people they serve. This customer’s product offerings aim to solve challenges in industrial automation, transportation, physical security, smart spaces, and mapping.
The customer had issues with wire bondable gold that other PCB manufacturers were not able to address. Other high-speed and multi-layer circuit board issues such as dielectric thickness and line widths were also a concern that needed a resolution.
The customer had a requirement for IPC Class 2 PCBs that had to meet these design and manufacturing challenges:
- LiDAR sensors are needed to operate in high-vibration environments. This applies to both microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) mirror-based which include many moving components, and solid-state sensors. This means the PCBs required for these sensors had to be vibration-resistant.
- Another constraint for these sensors is the operating temperatures which can vary significantly from room temperature. This means the PCBs used had to withstand thermal cycling without a decrease in performance. This is only possible by designing PCBs that are thermally efficient.
- The sensors need to relay continuous 3D point data. This required PCBs with an exceptional signal performance which needs expert optimization of dielectric thickness and line widths.
- The customer’s LiDAR sensors call for AuPd gold wire bonding which is a massive challenge for manufacturing with adequate quality. The reliability of wire bonding for PCBs is a critical factor that had to be considered.
The solution – Sierra Circuits’ quickturn PCBs
Sierra Circuits is known for its strict adherence to timelines, highly consistent and reliable delivery services. When the customer presented its PCB design and manufacturing challenges, Sierra had its team of experts on the task.
With Sierra Circuits, the customer got the quality they were looking for with regard to wire-bonded gold, which involves a highly challenging manufacturing process. Leveraging its vast expertise at hand, it was able to easily optimize dielectric thickness and line widths for signal performance. The responsive service provided by Sierra helped the customer eliminate downtime and boost productivity. The PCBs that Sierra Circuits delivered met the requirements for vibration resistance and thermal efficiency with great ease.
Sierra Circuits continues to aid its customers in innovating and commercializing LiDAR technology with its quickturn PCBs powering LiDAR sensors.

Design for Manufacturing Handbook
10 Chapters - 40 Pages - 45 Minute ReadWhat's Inside:
- Annular rings: avoid drill breakouts
- Vias: optimize your design
- Trace width and space: follow the best practices
- Solder mask and silkscreen: get the must-knows
Download Now